They remain fixed per unit of production but change in total based on the level of activity within the business. We have spent considerable time identifying and describing the various ways that businesses categorize costs. It is important not only to understand average total assets: what is formula calculation meaning the categorization of costs but to understand the relationships between changes in activity levels and the changes in costs in total. It is worth repeating that when a cost is considered to be fixed, that cost is only fixed for the relevant range.
Step Costs
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . If you’ve ever flown on an airplane, there’s a good chance you know Boeing.
Related AccountingTools Course
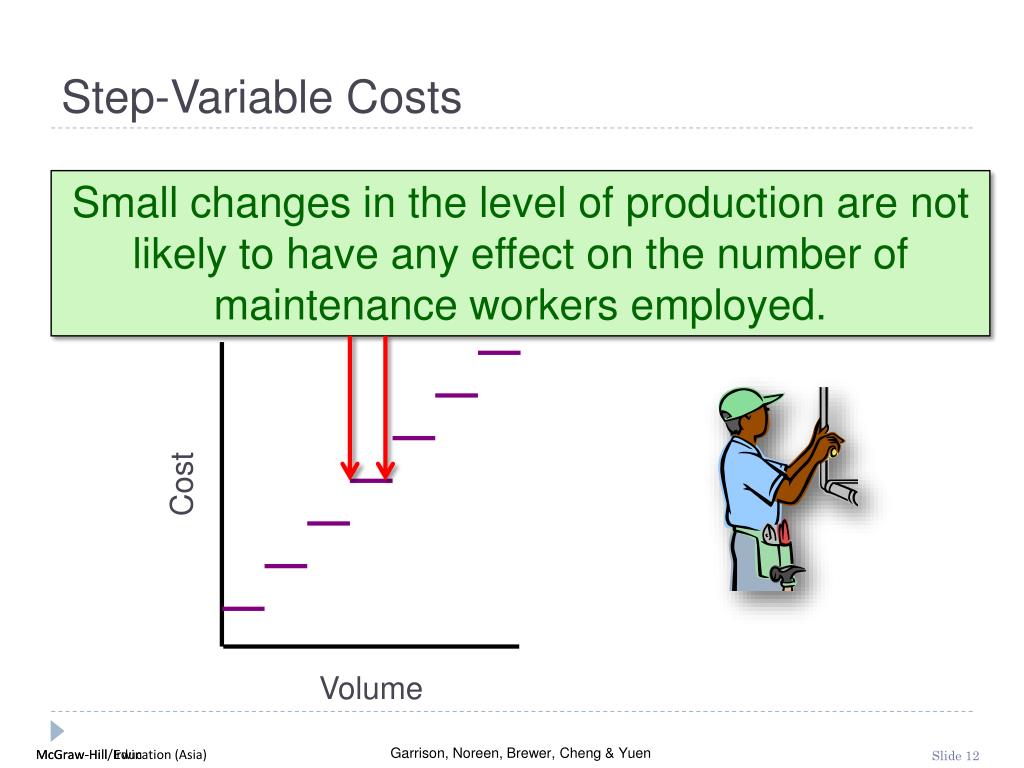
- Then, at certain points, the step costs increase to a higher amount.
- Many costs do not vary in a strictly linearrelationship with volume.
- Note that the Ocean Breeze mixed cost graph starts at an initial $2,000 for the fixed component and then increases by $5 for each night their rooms are occupied.
- For example, a cost can be say $100 up to 500units, increase to $185 for 501 to 1,000 units and to $260 if output crosses 1,000 units.
Both of these costs could potentially be postponed temporarily, but the company would probably incur negative effects if the costs were permanently eliminated. These classifications are generally used for long-range planning purposes. The relevant range is the range of production orsales volume over which the assumptions about cost behavior arevalid. For example, if a company’s sales were not doing well, management may sell off an entire production line. The step cost for several expenses would abruptly decrease since all expenses related to that production line would be cut.
What does stepped cost mean?
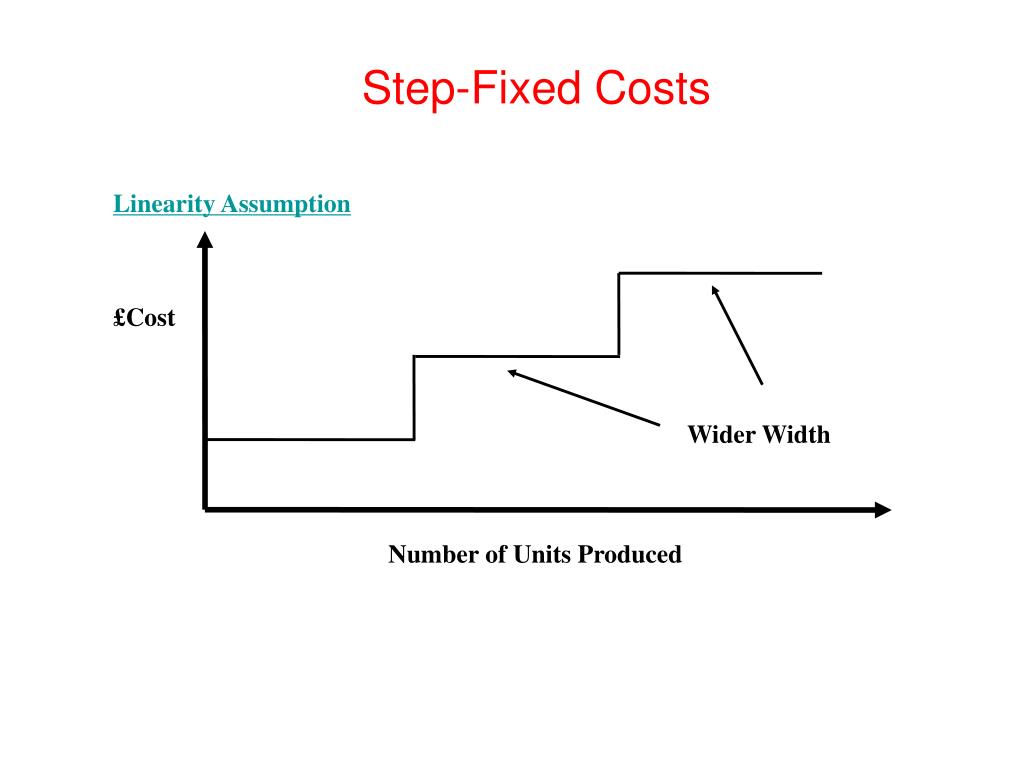
A cost that changes with the level of activity but is not linear is classified as a stepped cost. Step costs remain constant at a fixed amount over a range of activity. The range over which these costs remain unchanged (fixed) is referred to as the relevant range, which is defined as a specific activity level that is bounded by a minimum and maximum amount. Within this relevant range, managers can predict revenue or cost levels.
It may make sense to incur higher step costs if revenue is sufficient to cover the higher cost and provide an acceptable return. If the increase in volume is relatively minor, but still calls for incurring a step cost, profits may actually decline. If it’s just a small increase in volume, management may try to squeeze out extra productivity from existing operations, instead of incurring stepped-up costs.
Understanding Step Costs
The opposite is true, too—if business activity slackens, a material portion of costs will drop, with a step-down. A step variable cost is a cost that generally varies with the level of activity, but which tends to be incurred at certain discrete points and involve large changes in amounts when such a point is reached. Conversely, a truly variable cost will vary continually and directly in concert with the level of activity.
Remember that fixed costs are fixed over the relevant range, but variable costs change with the level of activity. If Bert wants to control his costs to make his bike business more profitable, he must be able to differentiate between the costs he can and cannot control. We see that total fixed costs remain unchanged, but the average fixed cost per unit goes up and down with the number of boats produced. As more units are produced, the fixed costs are spread out over more units, making the fixed cost per unit fall.
A step cost is also known as a stepped cost or a step-variable cost. Let us now discuss the formula to plot a step cost graph that shall act as a basis for our understanding of the concept and its related factors through the discussion below. For example, the depreciation on an ethanol facility is the same regardless of whether the facility is operated at 75% of capacity or 100% of capacity. A proper management and control over costs is crucial to maintain and grow profits which is the primary objective of every commercial business. The first step in achieving this is to understand the nature of costs that a business incurs while carrying out its operations as well as the factors affecting those costs. For a step cost to occur, the workload must either increase or fall below a certain threshold level.
This also leads to decreased demand for staff for those types of labor. Understanding step costs are useful because they help business owners decide whether rising above that threshold line would be a profit or loss to the company. While in the example Carolina Yachts is dependent upon direct labor, the production process for companies in many industries is moving from human labor to a more automated production process. For these companies, direct labor in these industries is becoming less significant. For an example, you can research the current production process for the automobile industry.

